Learn about how bees talk, from the waggle dance to pheromones. Read on to learn how human changes impact bees.
Introduction-
Bees, those tiny marvels buzzing around our gardens, have a language of their own. Unlike us, they don't use words but dance. It's a communication method that has fascinated scientists for years.
The Language of Bees
In the hive, where the heart of bee society beats, communication is crucial. When a forager bee discovers a good source of nectar, it doesn't keep the information to itself. Instead, it returns to the hive and performs a dance that tells its fellow workers exactly where to find the treasure.
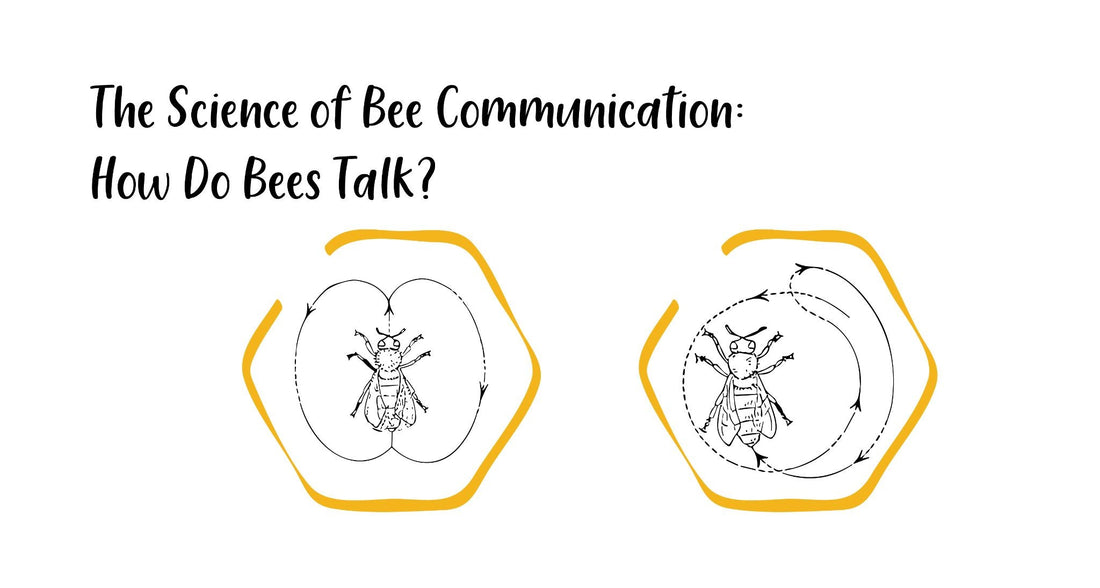
The waggle dance-
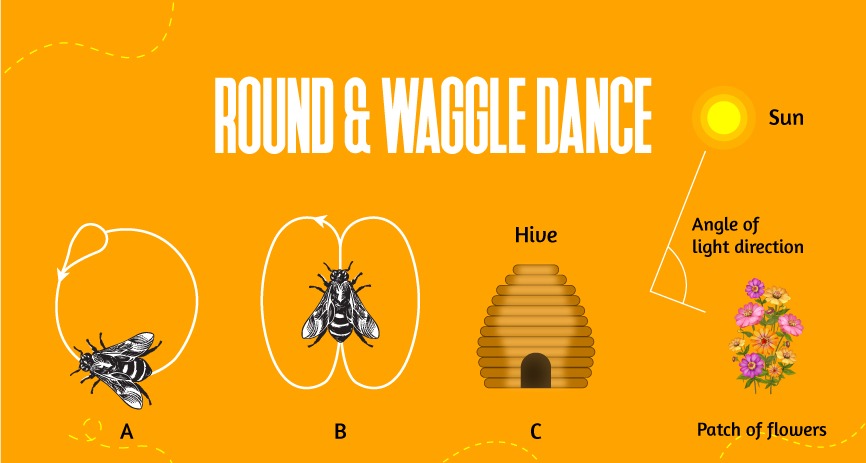
The waggle dance is like a living map that directs other bees to a specific location where a rich food source can be found. Picture a bee waggling its abdomen in a figure-eight pattern. The angle of the waggle relative to the vertical comb indicates the direction of the food source concerning the sun. If the dance is straight up, it means the food is towards the sun. The duration of the dance communicates the distance – longer dances indicate farther distances.

For example, if a bee discovers a field of vibrant flowers to collect nectar, it returns to the hive and performs the waggle dance to inform its fellow workers. The dance provides precise details, enabling other bees to navigate and locate the food.
The round dance-
On the flip side, there's the round dance, a simpler but equally effective communication method. Unlike the directional waggle dance, the round dance is more of a circular, excited movement. This dance signifies that the food source is nearby, within 50 meters of the hive. The absence of a specific direction in the round dance indicates that the other bees need to explore their surroundings to find food.
Both dances are crucial for the survival of the hive. They allow bees to communicate and coordinate their efforts in foraging and resource gathering. The simplicity and directness of these dances illustrate the remarkable efficiency of the bees' communication system.
Interestingly, bees aren't born knowing how to dance. Young worker bees learn these dances by observing and mimicking experienced foragers. The communal aspect of this learning process emphasizes the cooperative nature of bee colonies.
This dance language isn't just limited to food-related matters; it also plays a role in decision-making for a new nest site. When a swarm of bees is ready to establish a new colony, scout bees search for potential locations. Upon finding a suitable site, a scout returns to the swarm and dances to communicate the location of the potential nest. The intensity of the dance corresponds to the quality of the site.
Pheromones and chemical communication-
Pheromones play a crucial role in the world of bees, shaping their behavior and communication within the hive. These chemical signals, emitted by various glands in a bee's body, serve as a language that guides their social structure and activities.
The role of the queen bee-
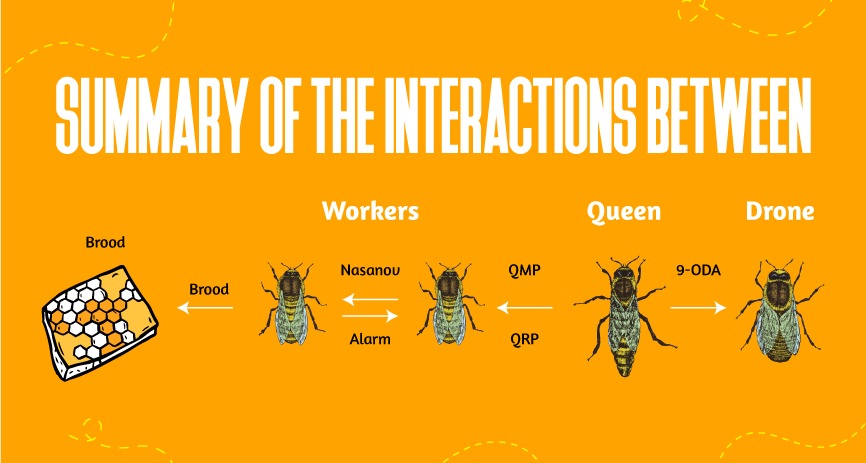
One essential function of pheromones is to maintain order in the hive. The queen bee's primary pheromone, known as the Queen Mandibular Pheromone (QMP), is her secret weapon. QMP is a complex blend of chemicals that conveys not only her presence but also her reproductive status and overall health to the rest of the colony. This pheromone is released by the queen's mandibular glands, located in her head, and it permeates the hive, shaping the behavior and functions of the worker bees.
The queen bee's communication journey begins with her nuptial flight. During this flight, she mates with multiple drones, storing their sperm in her spermatheca. As she returns to the hive, she carries the essence of this union in the form of QMP. The release of this pheromone communicates to the colony that the queen is present and fulfilling her role in the reproductive cycle of the hive.
One of the critical roles of QMP is to assert the queen's dominance and establish order within the hive. When the queen is healthy and thriving, she continuously emits QMP, creating a harmonious atmosphere. This pheromone acts as a reassuring signal to worker bees, indicating that their leader is present and all is well. In response to QMP, worker bees exhibit behaviors that maintain hive cohesion, such as inhibiting the development of new queens and promoting a sense of security among colony members.
Moreover, QMP plays a crucial role in suppressing reproductive activities among worker bees. In the absence of QMP, worker bees may develop ovaries and lay eggs, disrupting the hive's social order. The queen's pheromone serves as a regulatory mechanism, ensuring that only the queen engages in reproductive activities. This controlled reproductive system is vital for the hive's stability and overall functionality.

Worker bees also produce pheromones to communicate with each other. Alarm pheromones, released in response to a threat, act as a rapid alert system. When a bee stings an intruder, it releases an alarm pheromone that signals nearby bees to prepare for defence. This prompt communication helps the colony respond to dangers, ensuring the safety of the hive.
Furthermore, pheromones regulate the division of labor among worker bees. As the bees age, they transition through different tasks within the colony. Young bees, upon maturation, produce a pheromone signaling their readiness to take on foraging responsibilities. This chemical cue triggers a shift in their roles, contributing to the efficient functioning of the hive.
The process of trophallaxis, where bees exchange food among themselves, is also facilitated by pheromones. Bees release trophallactic pheromones during this food-sharing ritual, enhancing social bonds and communication. This communal dining not only nourishes the colony but also reinforces the interconnectedness of the bee society.
Recent Research and Discovery -
Complex Learned Social Behavior in Honey Bees' Waggle Dance (March 9, 2023):
Complex learned social behavior discovered in bee's 'waggle dance' | ScienceDaily
- Researchers at the University of California San Diego discovered early social learning in honey bees.
- The "waggle dance," a form of communication used by honey bees to signal the location of critical resources to nestmates, was found to be a form of social learning.
- The waggle dance, which involves specific motions indicating distance, direction, and quality of resources, is improved by learning and can be culturally transmitted among bees.
- Bees that did not have the opportunity to follow experienced dancers before their first dance produced more disordered dances, larger waggle angle divergence errors, and encoded distance incorrectly.
- This study highlights the importance of early social signal learning in honey bees, showcasing one of the most complex non-human spatial referential communication systems.
Impact of Human-Induced Changes on Bee Communication Strategies
Human factors affect bees' communication, researchers find
- Scientists at the University of Bristol studied honeybees, bumblebees, and stingless bees to understand variations in their communication strategies.
- Differences in communication strategies were attributed to variations in habitats and social lifestyles, such as colony size and nesting habits.
- Anthropogenic changes, including habitat conversion, climate change, and agrochemical use, were found to alter the world bees inhabit, affecting communication directly and indirectly.
- The study emphasizes that human-induced changes can interfere with bee communication and behaviors that have been crucial for their success for millions of years.
- Further research is needed to understand how habitat loss, climate change, and pesticides impact communication behaviors in bees.
Importance of bee communication-
Understanding bee communication holds significant implications for beekeepers and conservation efforts. Beekeepers can benefit from insights into the intricacies of the waggle dance, allowing them to optimize hive management and support the well-being of their colonies. Moreover, as external factors like habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use threaten bee populations, comprehending the nuances of bee communication becomes integral to conservation strategies. By addressing the challenges posed by human-induced changes to their environments, informed conservation efforts can help safeguard these pollinators, ensuring the continued health of ecosystems and agricultural productivity. The study of bee communication also provides practical tools for the stewardship and preservation of bee populations in an ever-changing world.
In the ever-changing world of bees, the study of communication provides practical tools for better understanding the bee colony. As for those seeking the purity of truly raw honey, HoneyAllDay stands as a brand committed to cold processed, authentic honey which you can have on-the-go with our honey pouches and honey straws.
How do bees communicate with each other?
Bees communicate primarily through the "waggle dance," which conveys information about the location of food sources, and through pheromones that signal different behaviors.
What is the waggle dance in bee communication?
The waggle dance is a figure-eight movement performed by bees to communicate the direction and distance of a food source to other bees in the hive.
Do bees use pheromones to communicate?
Yes, bees use pheromones to communicate various messages, including marking territory, signaling alarm, or identifying the queen and other members of the colony.
How do bees know which flowers to visit?
Bees use visual and olfactory cues to identify flowers. They communicate their findings to other bees using the waggle dance and pheromones, directing them to the best flowers.
Why is bee communication important for the hive?
Bee communication ensures efficient foraging, hive defense, and colony organization. It allows bees to share vital information and maintain the colony’s survival.
Explore nature's communication with HoneyAllDay – truly raw honey, anytime, anywhere.